Have you ever marveled at the delicate beauty of a glass teapot? How does such a fragile material transform into a functional piece of art? What mysteries lie in the process of its creation?
The art of glassmaking is an ancient tradition, yet it continues to fascinate us with its blend of creativity and science. In particular, the production of glass teapots represents a unique combination of these elements. This blog post aims to demystify the intricate process of glass teapot production, revealing the skill and precision involved in every step.

What Does it Take to Create a Glass Teapot?
Creating a glass teapot involves a detailed and meticulous process. It all starts with raw material preprocessing. This step involves crushing chunky materials like quartz sand, soda ash, limestone, and feldspar. The wet materials are then dried, and iron-containing materials are treated for iron removal to ensure the quality of the glass.
Next comes the batch preparation, where these materials are carefully mixed in precise proportions. The magic begins in the melting process, where the glass batch is heated at high temperatures (1550 to 1600 degrees Celsius) in a furnace. This step is crucial for forming a uniform, bubble-free liquid glass ready for molding.
The production of a glass teapot involves several key steps
- Raw Material Pre-processing: This involves crushing bulky raw materials like quartz sand, soda ash, limestone, feldspar, etc. The process also includes drying moist materials and removing iron from iron-containing materials to ensure glass quality.
- Batch Preparation: Here, the ingredients are mixed in the correct proportions to form the glass batch.
- Melting: The glass batch is heated at high temperatures (between 1550 to 1600 degrees Celsius) in a tank furnace or kiln. This process forms a uniform, bubble-free liquid glass that meets the requirements for molding.
- Molding: The liquid glass is then placed into molds to form the desired shapes of glass products, such as flat glass, various containers, etc.
- Heat Treatment: This step involves processes like annealing and quenching. It’s used to relieve or induce stress in the glass, phase separation, or crystallization, and to alter the glass’s structural state.
The Craft of Shaping Glass
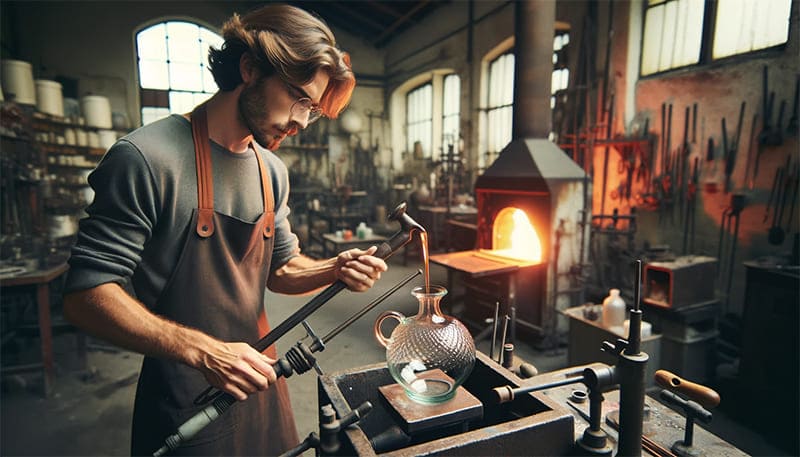

As for the specific technique of blowing glass to form glass teapots, there are two main methods: manual blowing and machine blowing.
Manual Glassblowing: A Dance of Skill and Precision
Manual Blowing: Also known as “blowing the bubble,” this technique was introduced to China from Central Asia in the 5th century. It involves dipping one end of a iron blowpipe into molten glass and then blowing air through the other end to shape the molten glass. The worker continuously rotates the blowpipe to prevent the glass from dripping and to shape it into the desired form. This process is intricate, requiring coordinated actions to achieve perfection. The size, thickness, and shape of the glass are controlled by the amount and speed of the air blown, as well as the rotation speed of the blowpipe.
Skills in hand-blown glassware
- Even distribution of the hot glass, relying on the appropriate rotation speed of the blowing iron.
- Proper timing and amount of blowing air, which is crucial for ensuring the correct size and thickness of the product.
- Consistent picking of the glass material, as the viscosity varies in different parts of the crucible.
Mould Blowing: Combining Tradition with Innovation
Mold Blowing: In contrast to freehand blowing, mold blowing involves using molds made of materials like copper or iron. The glassworker dips the blowpipe into molten glass and then blows it into the mold. This technique allows the creation of complex shapes and parts like handles, mouths, and bases of the vessel. Mold blowing enriches the variety and artistic nature of glass products.
Both methods are essential in the art of glassmaking and require significant skill and experience.
Mastering the Art of Welding in Glass Teapot Production
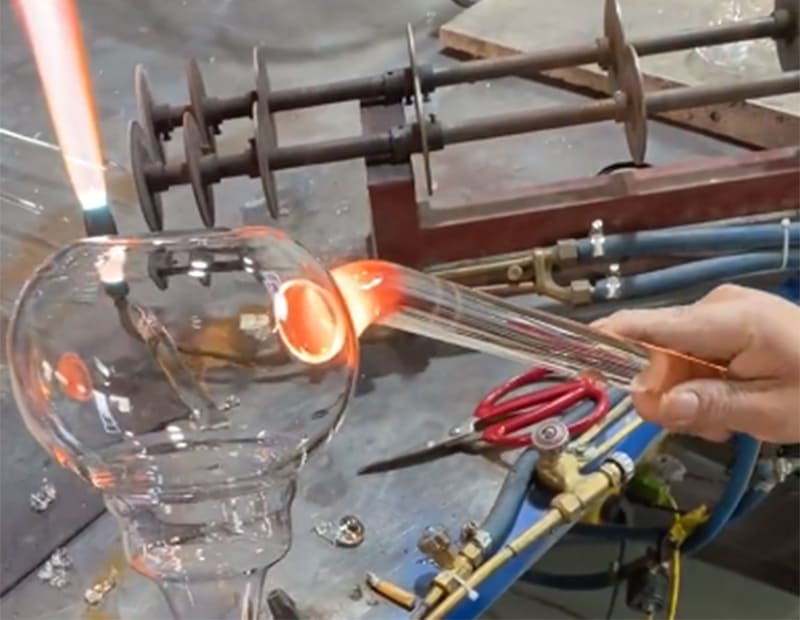
An essential yet often overlooked step in the creation of glass teapots is the welding process. This critical stage involves the meticulous joining of the spout, handle, and body of the teapot while the glass is in a hot, malleable state. It’s a task that requires precision, skill, and a deep understanding of the glass’s behavior under heat.
The Process of Welding Components
The welding process begins once the individual parts of the teapot – the body, spout, and handle – have been shaped and formed. These components are reheated to a temperature where the glass becomes pliable. The artisan then carefully aligns and joins these pieces. The key here is to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the parts to ensure a seamless and strong bond. If the temperature is too low, the glass won’t fuse properly, and if it’s too high, the glass can become too fluid and lose its shape.
Challenges and Solutions in Glass Welding
One of the main challenges in welding glass parts is avoiding thermal stress. Uneven heating or rapid temperature changes can cause the glass to crack, either during the process or later when the teapot is in use. To prevent this, artisans must ensure a uniform heat distribution and a gradual cooling process, known as annealing, after the welding is done.
Another challenge is achieving a clean, smooth join without compromising the teapot’s aesthetic appeal. Excess material at the joints can be unsightly and may also affect the teapot’s balance and functionality. Skilled artisans use tools like torches and tweezers to manipulate the molten glass, smoothing out any irregularities and ensuring a neat finish.
Preventive Measures for Quality Assurance
To ensure the quality and durability of the welded joints, several preventive measures are adopted. These include:
- Controlled Heating: Using specialized equipment to uniformly heat the glass parts.
- Precision Alignment: Carefully aligning the components before welding to ensure a perfect fit.
- Gradual Cooling: Allowing the welded teapot to cool slowly in a controlled environment, reducing the risk of thermal stress and cracks.
- Quality Inspection: Conducting thorough inspections at every stage, from the initial welding to the final product, to detect any flaws or weaknesses in the joints.
The welding process in glass teapot production is a testament to the blend of art and science in glassmaking. It requires not just technical expertise, but also an artistic touch to ensure that the final product is both functional and beautiful. By mastering this step, artisans contribute to the longevity and elegance of the glass teapots, making them cherished items for tea enthusiasts around the world. This step, often unnoticed by the end-user, is crucial in bringing the functional art piece to life, ensuring that each teapot is not only visually stunning but also durable and reliable for its intended use.
Essential Thermal Treatment
After the glass teaset is shaped, it undergoes an essential thermal treatment process, including annealing or quenching. This step is vital for relieving or inducing stresses within the glass, affecting its crystallization and structural state. It ensures the durability and safety of the teapot for use with hot beverages.
The Final Steps: Cleaning and Drying
Following the thermal treatment, the glass teapots enter the final stages of production: cleaning and drying. During production, teapots often accumulate dust, debris, or residual glass material. Cleaning ensures that each teapot is free from these impurities, maintaining their pristine and flawless appearance.
The drying process is equally critical. Packing teapots while damp could lead to water stains, marring their clear and luminous quality. Proper drying, therefore, is essential. It not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the teapots but also ensures they are ready for packaging and use.
These final stages of cleaning and drying underscore the meticulous nature of glass teapot production. They highlight the commitment to excellence, ensuring that each teapot is functional, beautiful, and ready to grace tables worldwide.
The Intricacies of Design and Functionality in Glass Teapots

When it comes to designing glass teapots, the process is not just about aesthetics but also functionality. Designers must consider how the teapot will be used, ensuring that it pours well and retains heat efficiently, all while showcasing the beauty of the glass. The shape, thickness, and even the curvature of the spout are meticulously planned and executed.
The Role of Color and Decoration in Glass Teapots
While many glass teapots showcase the natural, clear beauty of glass, color and decoration can add another dimension. Colored glass is made by adding metallic salts during the melting process. Techniques such as etching, engraving, or applying decals are used for decoration, each requiring additional steps and expertise.
The Importance of Quality Control in Glass Teapot Production
Quality control is crucial throughout the glass teapot manufacturing process. Each piece must be inspected for imperfections like bubbles, cracks, or uneven thickness, as these can affect the teapot’s strength and safety. The quality of the glass also impacts its clarity and brilliance, essential attributes of a high-quality glass teapot.
The Environmental Impact of Glass Production
While glass is a sustainable material, the production process has environmental implications. The high temperatures required for melting consume significant energy, and the raw materials must be mined and transported. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, like using recycled glass and implementing energy-efficient technologies, to mitigate these impacts.
The Evolution of Glass Teapots: From Ancient Craft to Modern Art

The art of making glass teapots has evolved significantly over the centuries. From the early days of manual glassblowing to today’s sophisticated manufacturing techniques, each era has contributed to the refinement of this craft. Modern glass teapots are not just kitchenware; they are a fusion of history, art, and technology.
The Future of Glass Teapot Production: Innovation and Trends
Looking ahead, the glass teapot industry is poised for further innovation. Advances in materials science may lead to even more durable and heat-efficient glass. Design trends are constantly evolving, with contemporary designs focusing on minimalism and functionality. The future may also see a greater integration of smart technology in glass teapots, enhancing the tea-drinking experience.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Art of Glass Teapots
The journey from raw materials to a finished glass teapot is a remarkable process, blending centuries-old techniques with modern innovation. Each teapot is not just a vessel for brewing tea but a symbol of the enduring allure and versatility of glass. As we use and admire these beautiful creations, we celebrate the art, science, and craft of glass teapot production.
The art of glass teapot production is a beautiful symphony of tradition and technology, requiring skill, precision, and creativity at every step. From the handling of raw materials to the final thermal treatment, each phase contributes to the creation of a functional and aesthetic masterpiece. It’s a craft that celebrates both the history and future of glassmaking, showcasing how this ancient art continues to evolve and inspire.









